Silanes
The Functions on Organic Compounds
The activated hydrogen such as hydroxyl group, amino group, carboxyl group, or amide group in the organic compounds can be substituted by silicon with the use of silylating agents. The purposes of substitution are as follows:
(1) To protect reactive group during chemical reaction
(2) To improve reaction selectivity
(3) To improve solubility in solvents
(4) To improve stability during distillation
(5) To improve applications for gas chromatograph and mass- spectrometry
At present, most uses are for the protection of the reactive group. Recently, many references have indicated preferential selectivity through use of a silylating agents. It is possible this application will gain more wide spread use in the near future. Silylating agents can protect against the reactive groups of alkaline reagents, oxidizing agents, reducing agents, Grignard reagents, and Wittig reagents used in the following processes.
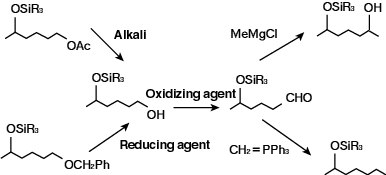
Selectivity
Introducing Trimethylsilyl Group
Compounds are selected for reaction in accordance with reactivity, by-products, and prices.
| KA-31 | The best general-purpose silylating agent, lowest price |
|---|---|
| HMDS | NH3 is the only by-product and no deposition of salts |
| TMST | The most powerful silylating agent, and can be used as a Lewis acid. |
Silylating Agent with Large Steric Bulk
| TESC | As a protective group, TESC is approximately 100 times more stable than KA-31 |
|---|---|
| TBMS | As a protective group, TBMS is approximately 10,000 times more stable than KA. Recommended for use under very severe reaction conditions |
*TBMS is solid at room temperatures, 50% toluene solution and 50% acetic acid ethyl solutions are usually available for industrial use.
The stability of silylated functional groups is affected by the bulkiness of the organic substituents. The stability of the silylated functional group can be estimated from Taft's 3D parameters (the greater the negative values the higher mass) in the following table.
Taft's 3D Parameters
| Substitution Group | ESSi |
|---|---|
| Me | 0 |
| Et | -0.261 |
| n-Pr | -0.315 |
| n-Bu | -0.348 |
| i-Bu | -0.400 |
| Me3CCH2 | -0.589 |
| i-Pr | -0.677 |
| s-Bu | -0.704 |
| c-C6H11 | -0.757 |
| Et2CH | -0.816 |
| t-Bu | -1.670 |
2Bi-Functional Silylating Agent
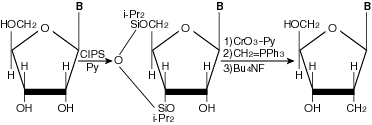
| CIPS | CIPS is best suited for use in protecting the hydroxyl group of polysaccharides and nucleosides, and is effective in the synthesis of 3' and 5' hydroxyl groups of nucleoside. CIPS is reactive bi-functionaly and selectively and is now used for developing nucleic acid anticancer agents and anti-HIV drugs. |
|---|
Examples of Applications
We have received many reports on the silylated agent, described are the applications of CIPS.